Django 模板
Django 模板
Django提供了一种便捷的方式来通过使用其模板系统生成动态的HTML页面。
模板包括所需HTML输出的静态部分,以及描述动态内容将如何插入的一些特殊语法。
为什么使用Django模板
在HTML文件中,我们不能编写Python代码,因为代码只能由Python解释器而不是浏览器解释。我们知道HTML是一种静态标记语言,而Python是一种动态编程语言。
Django模板引擎用于将设计与Python代码分离,并允许我们构建动态网页。
Django模板配置
要配置模板系统,我们必须在 settings.py 文件中提供一些条目。
TEMPLATES = [
{
'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'templates')],
'APP_DIRS': True,
'OPTIONS': {
'context_processors': [
'django.template.context_processors.debug',
'django.template.context_processors.request',
'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth',
'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages',
],
},
},
]
这里,我们提到我们的模板目录名为 templates 。默认情况下,DjangoTemplates在每个INSTALLED_APPS中查找一个 templates 子目录。
Django模板简单示例
首先,像下面我们所做的那样,在项目应用程序中创建一个目录 templates 。
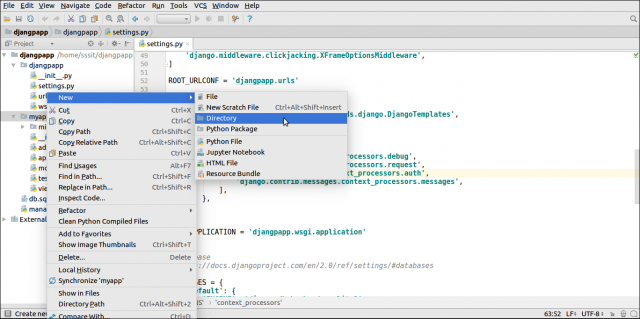
在创建的文件夹中创建一个模板 index.html 。
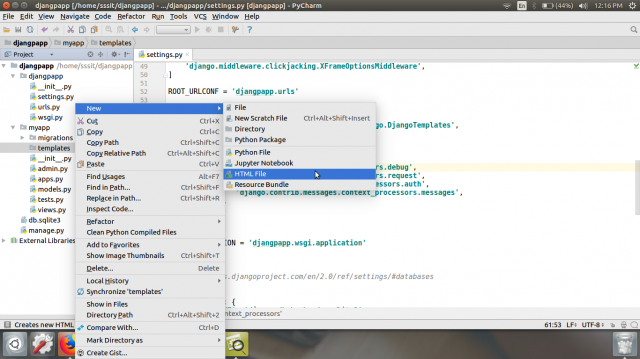
我们的模板 index.html 包含以下代码。
// index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Index</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Welcome to Django!!!</h2>
</body>
</html>
加载模板
要加载模板,调用get_template()方法,如下所示,并传递模板名称。
//views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
#importing loading from django template
from django.template import loader
# Create your views here.
from django.http import HttpResponse
def index(request):
template = loader.get_template('index.html') # getting our template
return HttpResponse(template.render()) # rendering the template in HttpResponse
在浏览器中设置一个URL来访问模板。
//urls.py
path('index/', views.index),
在INSTALLED_APPS中注册应用程序
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'myapp'
]
运行服务器
执行以下命令,并在浏览器中输入以下地址来访问模板: localhost:8000/index
$ python3 manage.py runserver
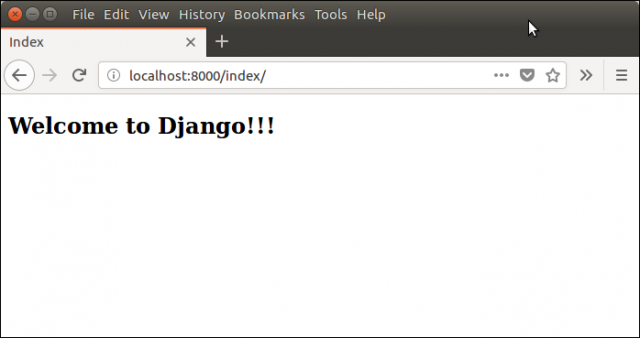
Django 模板语言
Django 模板使用自己的语法来处理变量、标签、表达式等等。模板会用上下文渲染,在网页中获取值。请参见示例。
变量
与上下文相关联的变量可以通过{{}}(双花括号)进行访问。例如,一个变量名是 value,其值为 rahul。那么以下语句将用其值替换 name。
My name is {{name}}.
My name is rahul
Django变量示例
//views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
#importing loading from django template
from django.template import loader
# Create your views here.
from django.http import HttpResponse
def index(request):
template = loader.get_template('index.html') # getting our template
name = {
'student':'rahul'
}
return HttpResponse(template.render(name)) # rendering the template in HttpResponse
//index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Index</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Welcome to Django!!!</h2>
<h3>My Name is: {{ student }}</h3>
</body>
</html>
输出:
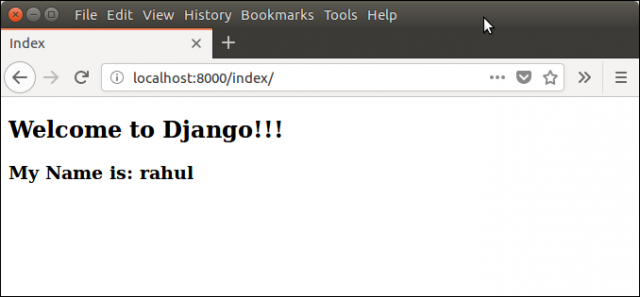
标签
在模板中,标签为渲染过程提供任意的逻辑。例如,一个标签可以输出内容,充当控制结构(如一个“if”语句或“for”循环),从数据库获取内容等。
标签使用{% %}括起来。例如:
{% csrf_token %}
{% if user.is_authenticated %}
Hello, {{ user.username }}.
{% endif %}
本文链接:http://so.lmcjl.com/news/17613/